Ankle-brachial index
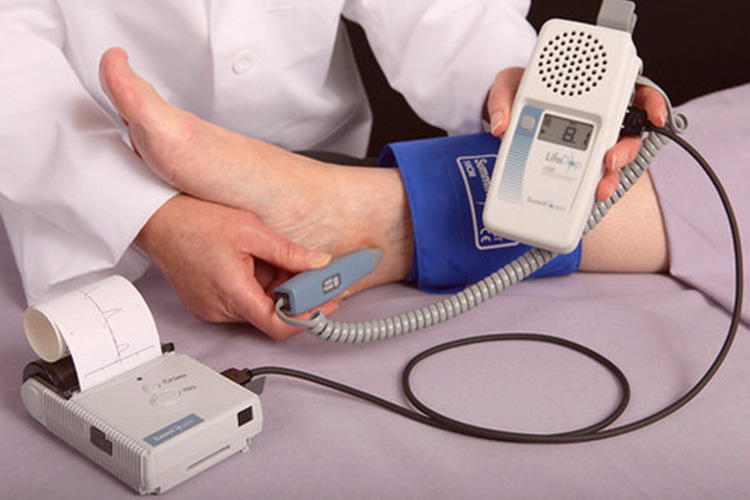
Exam that addresses the relationship of blood pressure between upper and lower limbs, measured with a vascular doppler, useful for estimating cardiovascular risk and for investigating obstructions in lower limb arteries, in peripheral arterial disease.
Indirect Calorimetry
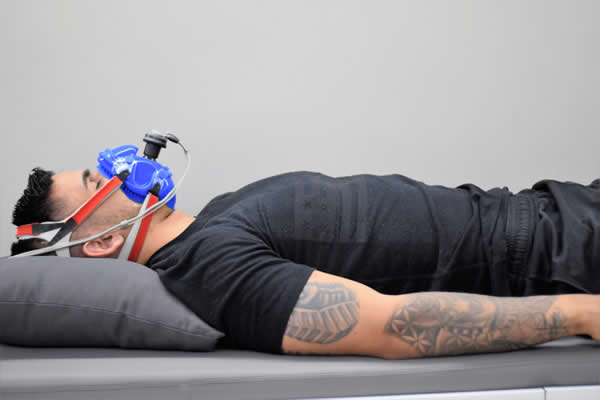

This test measures the amount of energy that your body expends at rest. The estimation of calories consumption needed is fundamental to plan the desired aim of losing or gaining or keeping the ideal body weight.
Cardiopulmonary stress test

Similar to exercise testing, this exam adds simultaneous assessment of exhaled gases, providing a direct, and not estimated, measure of aerobic capacity, particularly the maximum oxygen consumption. It also provides other important parameters for prescribing recreational or programmed exercise, aiming high performance or chronic disease rehabilitation.
Exercise Test
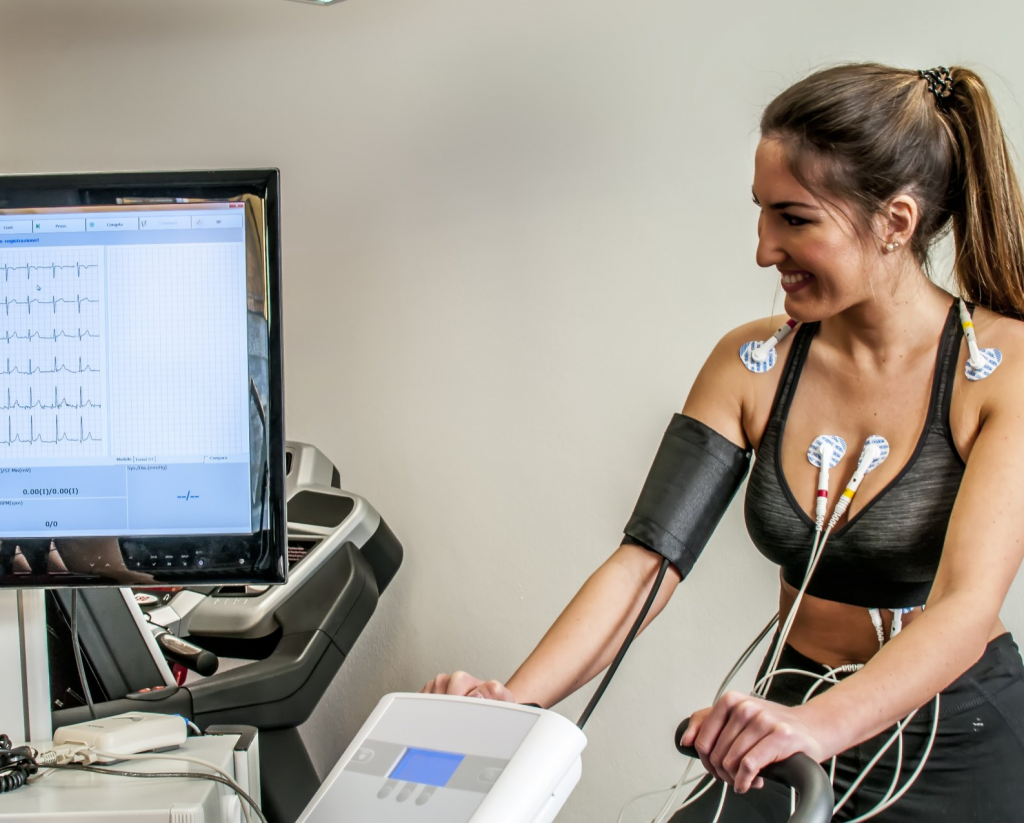

The exercise test shows the heart and blood pressure responses to acute physical stress. We check for possible silent ischemia, blood pressure responses and estimated functional capacity, with data that complement the clinical assessment regarding the establishment of cardiovascular risk.
ECG

The electrocardiogram instantly checks for changes in rhythm, electrical conduction, possible electrical changes due to lack of oxygenation of the heart muscle or adaptations resulting from other diseases such as high blood pressure or heart failure.
Abpm

The ambulatory blood pressure monitoring test serves to assess the behavior of blood pressure throughout 24 hours. It provides valuable information about blood pressure fluctuations while awake, while sleeping, verifies the “white coat” effect and whether the treatment is appropriate or needs adjustments.
Holter
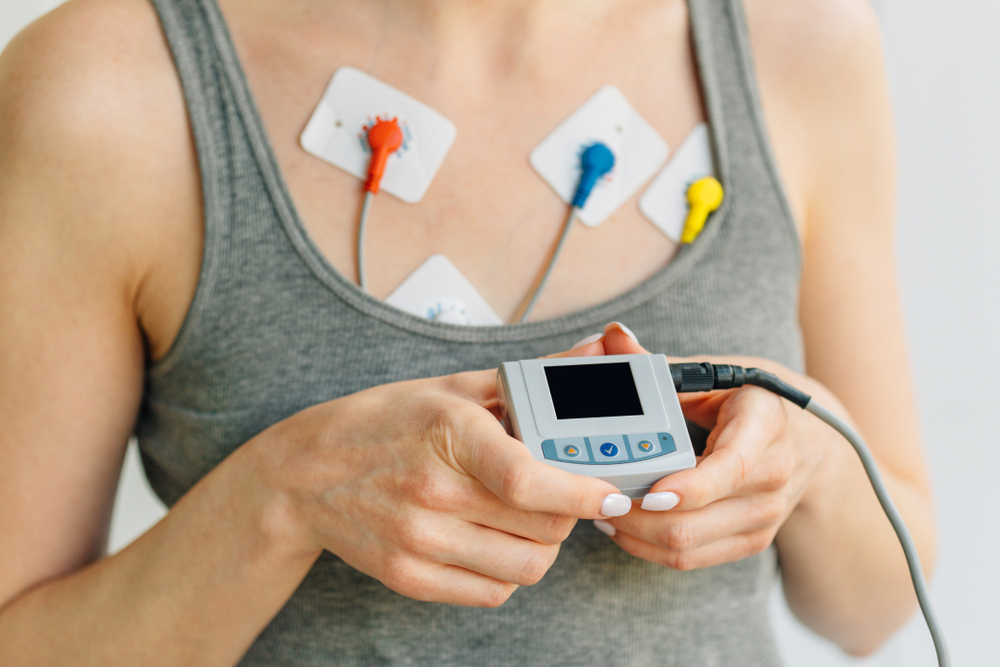
This exam is used to check the changes in heart rhythm over 24h, investigating hidden arrhythmias, heart beat behavior during sleep and during daily activities.
Pre-operative evaluation and Hospital follow up

Follow up of the entire patient journey from pre-operative preparation of cardiac and non-cardiac surgeries and hospital visits when demanded.
Clinical follow-up and prevention

Identification of risk factors which can lead to cardiovascular diseases, helping to strategize preventive plans to avoid complications.
Consults
Understand patients’ needs and propose ways to approach them, accounting for individual principles and time appointments.

